Traffic Speed Estimation from Surveillance Video
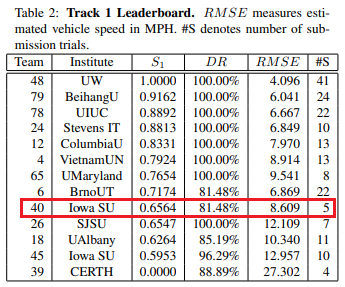
2018 AI City Challenge Track 1 Rank
Abstract
- Faster R-CNN with ResNet101을 이용하여 multi-object detection
- histogram comparison을 이용하여 object tracking
- pixel domain에서 real world의 speed를 구하기 위해 warping method를 적용
- 위 approach를 통해 intersection에서 vehicle speed estimation
1. Introduction
- vehicle speed estimating from video data
- multi-object detection → tracking → converting speed
- Multi-object detection
- Faster R-CNN with ResNet 101 as backbone
- Tracking
- Multi-object tracking(MOT), OpenCV provides tracking algorithms, such as MIL, BOOSTING, TLD, KCF…
- But, this paper proposes a histogram-based tracking algorithm
- Converting speed
- Image warping to convert the perspective from one way to another
- linear perspective transformation warping
- Multi-object detection
2. Data description
Track 1 data description, 2 highway ICs(Interchange) and 2 intersections
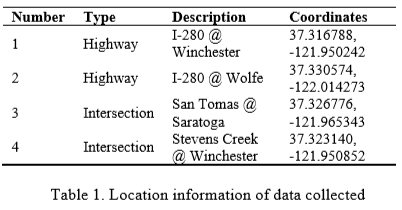
- video resolution is 1920x1080
- All cameras have overhead view
3. Methods and results
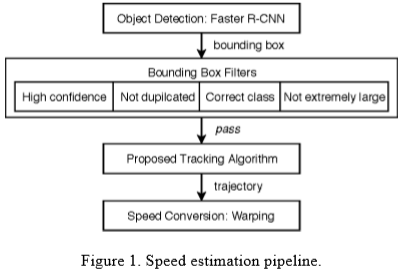
3.1. Object detection
- challenge에서 주는 training data가 부족하여 pre-trained object detection model을 사용함.
- TensorFlow object detection API에서 제공하는 여러 pre-trained model 중 하나를 선택함. .inference speed와 performance 측면을 고려하여, COCO dataset으로 학습된 Faster R-CNN with ResNet 101을 사용
- COCO dataset에서 “car”, “bus”, “truck” class만 사용
false positive를 줄이기 위해 “class filter”, “confidence score filter”, “duplicated detection filter”, and “outlier filter”까지 총 4가지 filter를 적용하고 이를 group filtering algorithm이라 부름
- Class filter
- COCO data에서 차량과 관련된 class는 car, bus, truck 3개뿐이므로 그외 77개 class는 필요없음. 따라서 class filter는 위 3개의 class를 제외한 나머지 class는 걸러내는 역할.
- Confidence score filter
- detection 과정에서 threshold를 0.2로 설정하여 충분한 양의 detection이 이루어지도록 함
- Duplicated detection filter
- IoU threshold 0.3으로 설정하여 중복된 detection을 지움
- Outlier filter
- extremely하게 큰 bounding box가 생길 수 있는데 이러한 box도 지워버림
- Applying filtering algorithm
(a), (b), (c)에서 멀리 있는 차량에선 중복된 bounding box가 많이 만들어지지만 제안하는 filtering 알고리즘을 통해 이를 보완할 수 있음
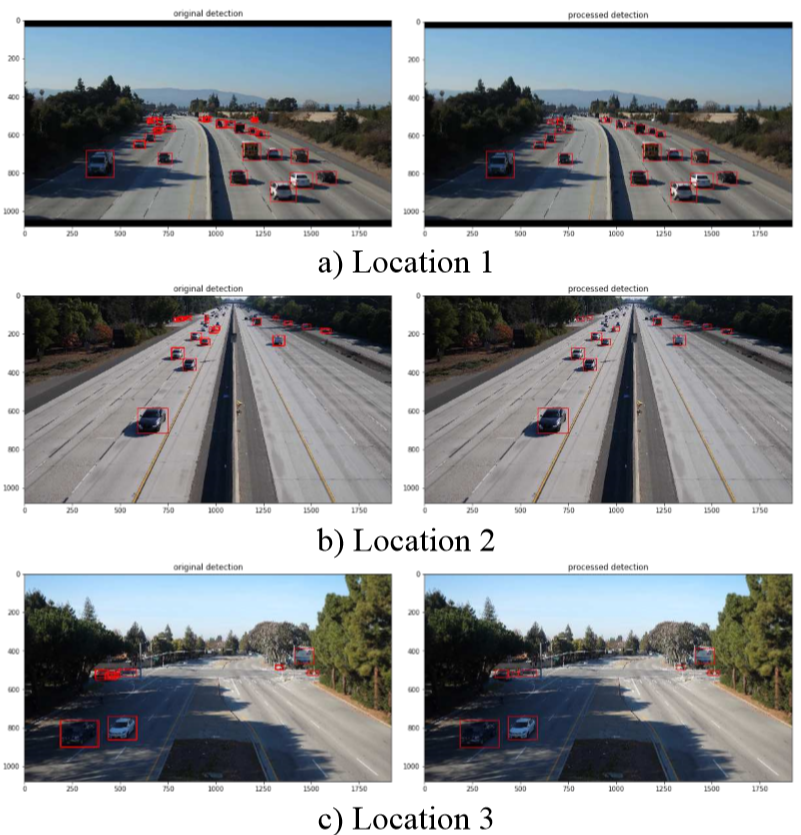

또한 아래 (d)에서처럼 extremely large bounding box가 만들어질 수 있는데 이러한 box들도 사전에 filtering

3.2. Multi-object tracking
- propose histogram-based tracking algorithm.
- histogram-based tracker는 연속된 frame에서 같은 object를 connect
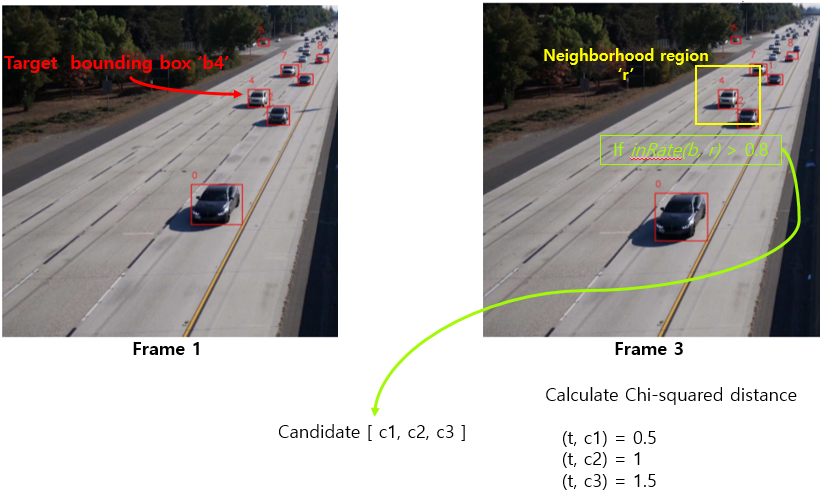
같은 object인지 아닌지 어떻게 판단? → histogram domain에서 minimum Chi-squared distance를 계산하여 frame간의 동일한 object를 tracking
Tracking Algorithm

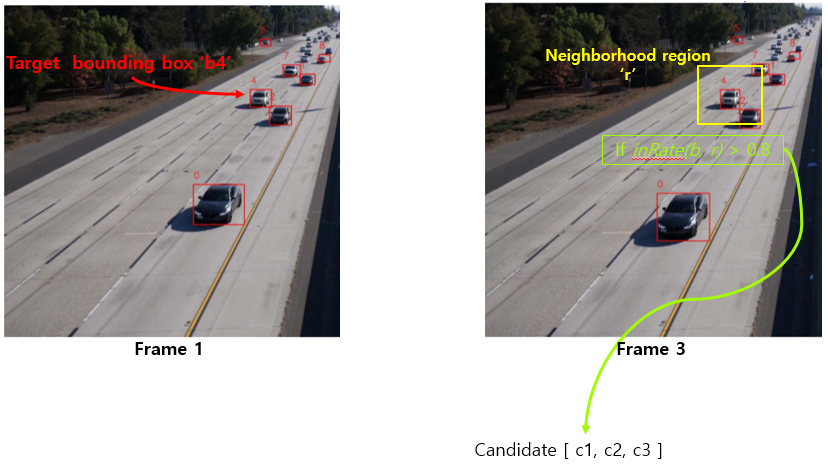
첫번째 frame에서 object detection으로 bounding box를 그리고 box마다 ID할당. frame 3에서 bounding box ID는 없다고 가정.

frame 1에서 ID가 4인 b4를 target으로 설정하고 이 차량을 어떻게 tracking하는지 보자.

frame 1에서 bounding box ‘b4’의 size를 extend시킨 ‘neighborhood region’을 frame 3에 그린다.
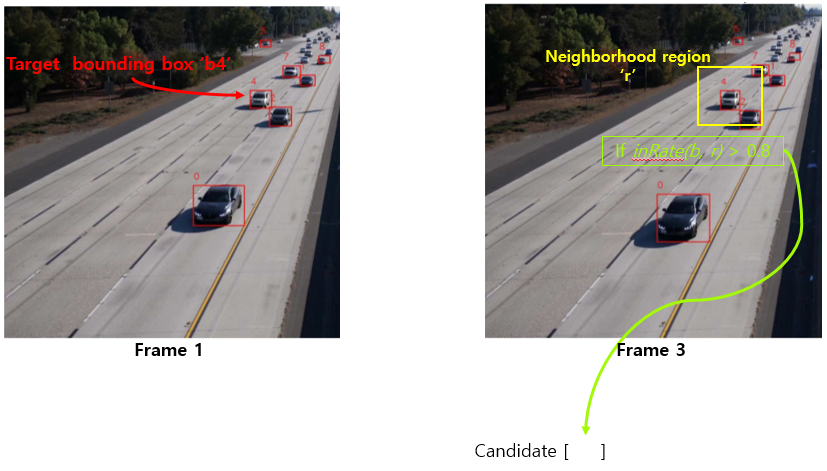
frame 3에서 만들어진 neighborhood region과 80% 이상 겹치는 bounding box들을 candidate로 설정한다. 총 3개의 box가 candidate로 들어갔다고 하자.
여러 candidate 중 하나만 선택해야하므로 frame 1의 target과 frame 3의 candidate 간의 Chi-squared distance를 계산하여 가장 작은 값을 최종 candidate로 선택한다.
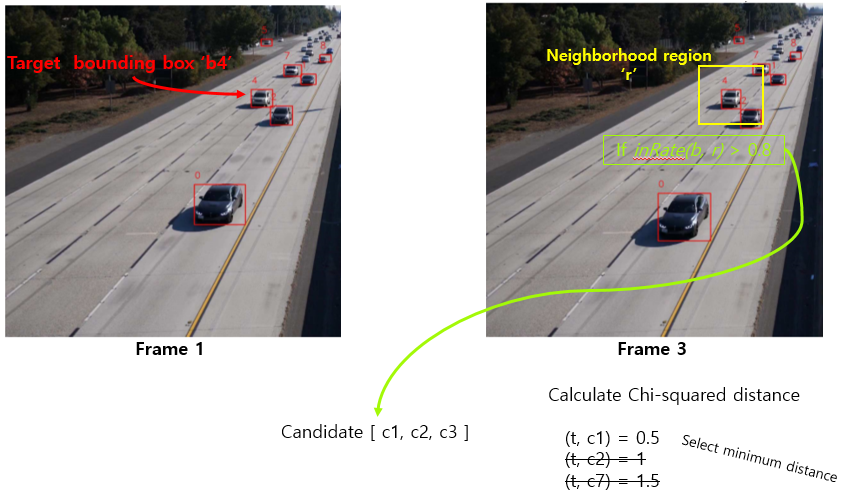
frame 3에서 선택된 최종 candidate에 target이 가지고 있던 ID와 같은 ID를 할당한다.
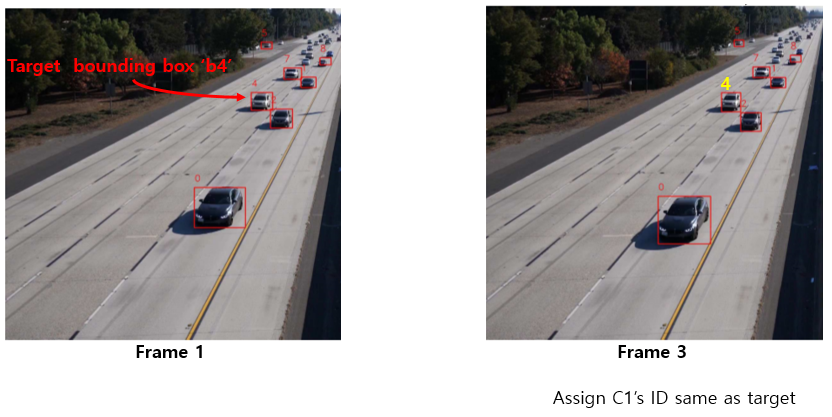

- frame 3에 존재하는 모든 bounding box들에 대해 위와 같은 방식으로 ID를 할당한다.
만약, ID가 할당되지 않은 경우 frame 1에서 나타나지 않고 frame 3에서 새롭게 나타난 차량으로 보고 새로운 ID를 할당한다.
Tracking result.
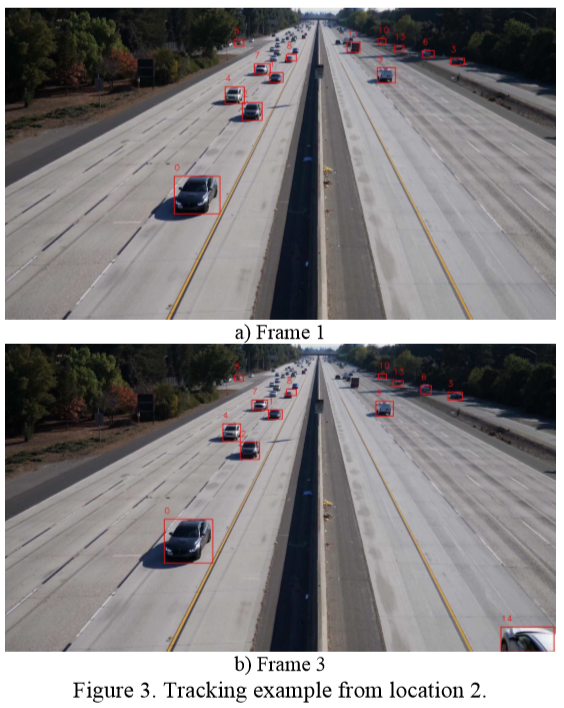

3.3. Speed conversion
pixel domain에서 mile per hour로 speed converting하기 위해 linear perspective transformation warping을 사용함.

- lane width를 12 feet로 가정(US standard)하여 warping된 lane에서 speed를 계산함. speed conversion result는 5 frame step size(0.167 second)로 moving average를 통해 smoothing
- 논문에선 linear perspective transformation warping method를 사용했는데 이 방법은 도로가 직선이거나 평평하거나 카메라 외곡이 없을 시, 오히려 error가 더 높아지는 원인이 될 수도 있음
- 따라서 warping method가 반드시 필요한 것은 아니며 향후 연구에서 pixel-to-reality calibration method를 사용하여 개선하는 것이 필요.
- 고속도로에선 신호가 없기 때문에 stop-and-go pattern이 거의 나타나지 않고 운전자들이 제한속도에 맞춰 주행한다고 가정할 수 있다. 따라서, linear perspective transformation으로부터 검출된 속도를 essential speed로 볼 수 있다. 또한 scaling method를 적용하여 final detected speed가 고속도로의 제한속도를 잘 따르도록 만든다.
- 고속도로와 달리 intersection에선 신호가 있기 때문에 stop-and-go pattern이 항상 나타난다. 따라서 smoothing method만 적용하고 별도의 processing은 적용하지 않는다. (여기서 말하는 smoothing은 speed conversion에서의 moving average smoothing을 의미하는듯)
4. Conclusion
- This study aims to solve the 2018 AI City Challenge Track 1.
- 3-step으로 접근
- multi-object detection using Faster R-CNN
- multi-object tracking based on histogram comparison
- speed conversion using warping with linear perspective transformation
- Detection과 tracking 결과는 plausible하지만 warping으로 인한 error가 발생할 수 있음
- warping으로 인한 limitation을 overcome하기 위해 고속도로 traffic은 free flow condition임을 가정하여 scaling method를 적용
- highway에선 speed estimation performance가 잘 나오는데 적용한 방법은 strict assumption and low scalability 하다는 단점이 있음.