Abstract
- Single-stage object detection method들은 real-time capability와 high accuracy로 인해 지속적으로 연구되어 왔음
- 일반적으로 single-stage detector는 2가지 특징을 갖는다.
- ImageNet으로 pre-training된 backbone network를 사용하는 것
- multi-scale feature를 다루기 위해 top-down feature pyramid representation 방식을 사용하는 것
- pre-training backbone을 사용하지 않고 네트워크를 처음부터 학습시키면 classification 과 localization task 사이의 gap을 줄일 수 있는 장점이 있음, 그러나 시간이 너무 오래걸리는 단점이 있음
- 본 논문에서는 pre-trained model을 fine-tuning하는 것과 training from scratch로부터 얻을 수 있는 advantage를 combine하는 새로운 single-stage detection framework를 제안한다.
- 또한, 일반적으로 사용하는 top-down pyramid representation 방식은 top layer의 high-level semantic 정보를 bottom layer로 passing하는 것에만 초점을 맞추는데 우리는 low/mid level과 high level semantic 정보를 효율적으로 circulate하는 bi-directional network를 제안한다.
1. Introduction
- 현재 object detection method는 크게 single-stage, two-stage로 구분할 수 있으며 single-stage method는 speed에서, tow-stage method는 accuracy에서 큰 이점을 가짐
- single-stage method의 속도를 살리면서 높은 정확도를 얻기 위한 연구가 있었음, large, medium size의 object는 잘 검출하지만 small object를 검출하는데 있어선 여전히 성능이 낮다.
small object를 잘 검출하기 위해선 low, mid-level information이 중요함
- SOTA single-stage method들은 주로 ImageNet으로 pre-training된 VGG, ResNet을 backbone으로 사용함. 그러나 classification-based pre-trained model과 localization에는 여전히 task 측면에서 gap이 존재함
- 위와 같은 gap을 줄이기 위해 training from scratch를 통해 localization에 더 초점을 맞춰 괜찮은 성능을 내는 결과도 있었지만 학습시간이 너무 오래걸린다는 문제가 있음
- 따라서 본 논문에서는 pre-training model과 learning from scratch로 부터 얻을 수 있는 advantage를 combine하는 새로운 framework을 제안한다.
pre-trained standard network를 사용하되 learning from scratch를 위한 auxiliary network를 추가하여 low-level, mid-level information을 보완한다. auxiliary network를 통해 small, medium object에 대한 정확도를 개선할 수 있음
- small object에 대한 성능을 높기이 위해 top-down pyramidal feature 방식을 많이들 사용한다. 이 방식은 high-level information(later layer’s feature)을 semantically weaker high-resolution feature(bottom or former layers)와 결합하는 방식임
- top-down feature pyramid 방식으로 성능을 개선했지만 이러한 방식은 그저 high-level semantic을 former layers에 layer-by-layer 형태로 inject하기만 한다는 점이 단점(?)이라고 할 수 있음
따라서 high-level information을 former layer와 결합하는 방식뿐만 아니라, low & mid-level information을 later layer와 결합하는 것이 multi-scale object detection에서 중요하다는 것을 주장함
- Contribution은 다음과 같다.
- we introduce a light-weight scratch network (LSN) that is trained from scratch taking a down-sampled image as input and passing it through a few convolutional layers to efficiently construct low-/mid-level features. These low-/mid-level features are then injected into the standard detection network with the pre-trained backbone.
- Further, we introduce a bi-directional network that circulates both low-/mid-level and high-level semantic information within the detection network.
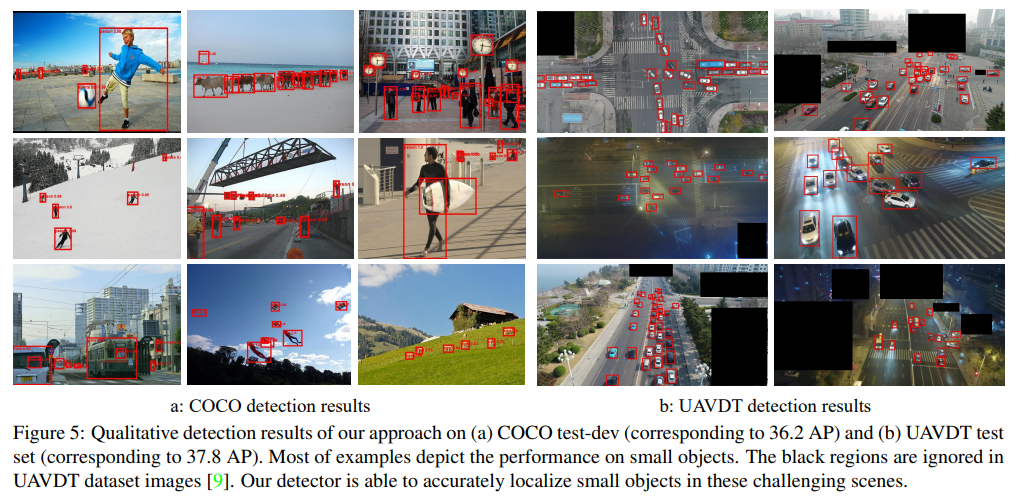
MS COCO, UAVDT(Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) dataset에서 superior performance를 달성함
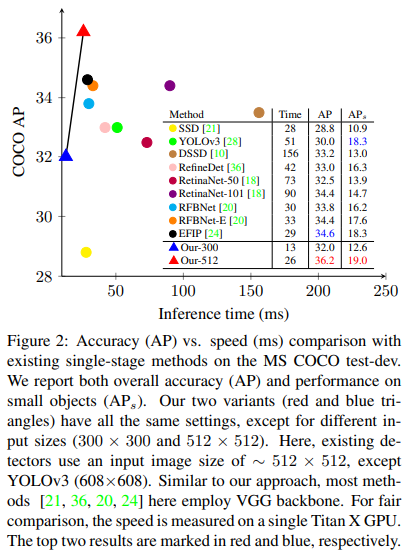
2. Baseline Fast Detection Framework
high speed, detection accuracy 측면에서 combined advantage가 있기 때문에 baseline으로 SSD를 사용한다.
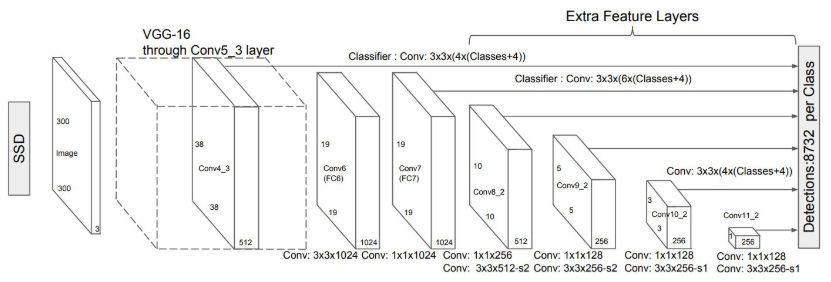
- SSD는 pyramidal feature hierarchy 구조로 독립된 convolution layer의 feature를 가져와서 prediction을 수행한다.
- SSD는 구조상 high-resolution feature에서 small object를 검출하도록 설계되었는데 이러한 low-level feature는 semantic information이 부족하다는 단점이 있다.
3. Our Approach
제안하는 모델은 크게 SSD, LSN(light-weitght scratch network) and bi-directional network 3가지 main component로 구성되어 있음
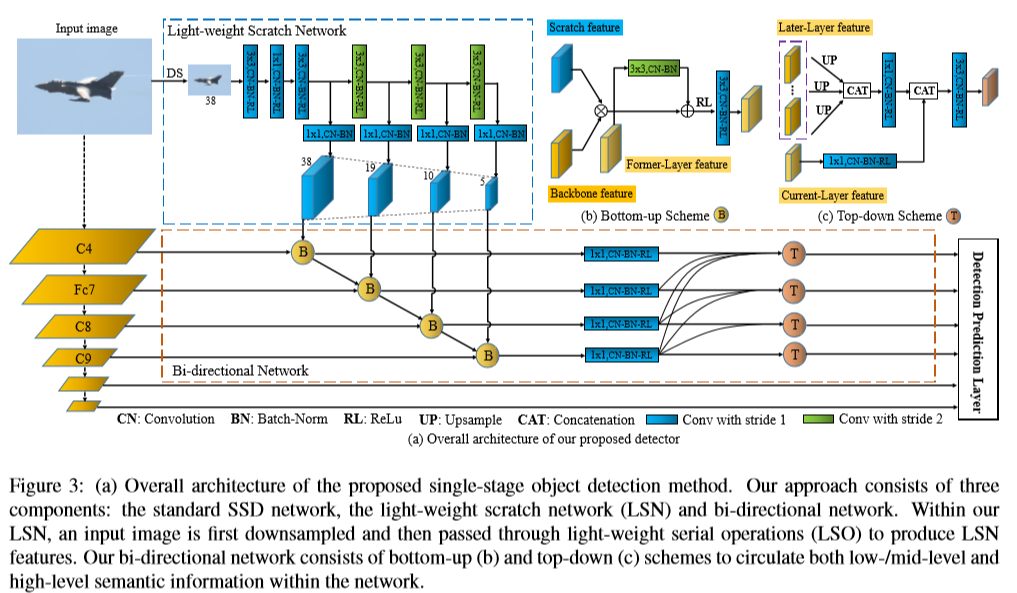
- standard SSD는 VGG16을 pre-trained network backbone으로 사용한다.
- Light-weight scratch network(LSN)은 low & mid level feature를 생성하는 역할을 하며 SSD의 feature와 결합되어 performance를 향상시키는 용도로 사용된다.
- Bi-directional network에선 current layer feature와 former layer feature가 bottom-up 방식으로 결합된다. 이후 top-down scheme에서는 current layer feature에 high-level semantic information(layer layer)을 가져와서 결합한다.
- 제안하는 bottom-up scheme는 기존의 FPN/SSD의 bottom-up part에서 cascade 방식으로 former layer에서 later layer로 feature를 propagate하는 operation을 추가함
- FPN에서 top-down pyramid는 여러 CNN layer들이 layer-by-layer 형식으로 fusion되는 방식이었지만, 제안하는 bi-directional network에선 independent parallel connection을 결합하여 prediction layer를 설계하였음
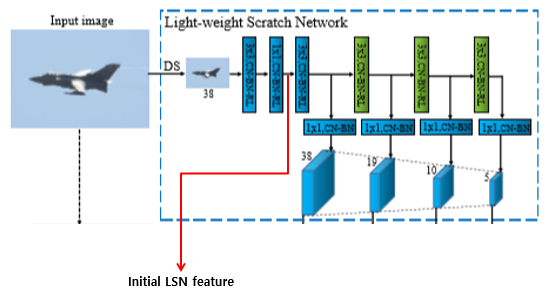
3.1. Light-Weight Scratch Network
- 제안하는 light-weight scratch network(LSN) 구조는 심플하면서 SSD prediction layer와 tight하게 연결된다. LSN의 주 역할은 low & mid level feature representation construction이라 할 수 있다.
일반적으로 Image classification에선 convolution, pooling layer를 여러 개 쌓아 네트워크를 구축하여 semantically strong feature를 추출한다. 그러나, image classification과 달리 object detection은 object에 대해 정확한 delineation이 필요하기 때문에 low & mid-level information이 매우 중요한 역할을 한다.
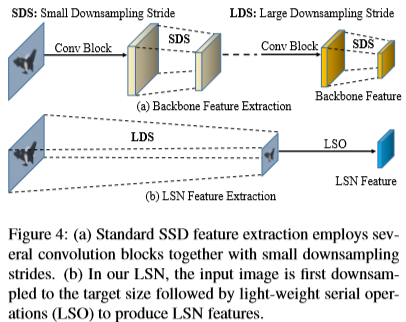
- 따라서 backbone으로 pre-trained network를 사용했을 때 발생하는 information loss를 보완하기 위해 LSN이 alternative feature extraction을 위한 역할을 수행한다.
- Input image를 바로 down-sampling(max-pooling 3번)하여 SSD first prediction layer의 target size와 맞춰준다. 그런 다음 LSO(light-weight serial operation)인 conv, bn, relu를 거쳐 LSN feature를 생성한다. LSN은 random initialization으로 초기화함.
- LSN feature를 SSD prediction layer와 연결하기 위해 38x38, 19x19, 10x10, 5x5 크기의 feature를 추출한다. Input image I에 대해 down-sampling된 I_t를 입력으로 하여 총 4개의 LSN feature s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4을 추출한다.
initial \; feature\quad s_{int(0)} = \varphi_{int(0)}(I_t)- I_t = down-sampled image
- 𝝋_int(0) =3x3 conv, 1x1 conv
- 𝝋_int(k) = 3x3 conv
- 𝝋_trans(k) = 1x1 conv
- k=0일 때, 즉 𝝋_int(0) operation에서만 3x3 conv, 1x1 conv 동시에 수행하고 그 이후(k≥1) 𝝋_int(k) operation은 3x3 conv만 수행함
- 𝝋_trans에서 따로 1x1 conv를 수행하고 이 연산은 SSD prediction feature와 채널수를 맞춰주기 위해 사용
3.2. Bi-directional Network
Bi-directional network의 역할은 low & mid-level feature와 high-level semantic information이 detection network 내에서 circulate 되도록 만드는 것이며 이를 위해 bottom-up and top-down scheme 2가지로 나누어진다.

- Figure 3를 다시 보자, bottom-up scheme에서는 backbone(SSD) feature와 LSN feature, former-layer feature를 결합한다. (그림으로 보는 게 더 이해 잘 됨)
Bottom-up scheme의 task를 BFP(bottom-up feature propagation)라 부르며 k번째 forward feature는 아래 수식으로 표현할 수 있다. 단, f_1을 구할 땐 forward feature를 사용하지 않으므로 w_(k-1) f_(k-1)이 없음.
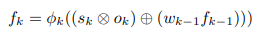
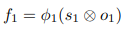
- s_k = k번째 LSN feature
- o_k = k번째 SSD prediction backbone feature
- w_(k-1) = 3x3 conv
- f_(k-1) = forward feature from (k-1)번째 level
- 𝝓 = ReLU and 3x3 conv
Bottom-up scheme forward feature pyramid
- bottom-up scheme는 low & mid-level feature를 circulate하는 역할을 하며 high-level semantic information을 inject하기 위해 top-down scheme를 사용한다.
- top-down scheme에서는 later layer feature를 모두 가져와서 current layer에 connect한다. 따라서 high-level semantic information이 independent parallel connection을 통해 circulate된다.
top-down scheme pyramid feature를 backward feature pyramid라 부르며 top-down scheme안에서 이루어지는 연산은 아래 수식으로 표현할 수 있다.
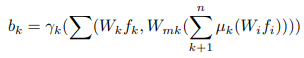
- f_i = forward feature (bottom-up scheme 거쳐서 나온 feature)
- W_i = 1x1 conv (feature channel 수를 줄이기 위해 사용)
- W_mk = 1x1 conv
- µ_k = upsampling (저자의 논문구현 코드에서 bilinear upsampling을 사용함)
- γ_k = 3x3 conv
- Σ = concatenation
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
- Dataset MS-COCO, UAVDT
- UAVDT dataset
- object of interest in this benchmark is “vehicle”
- category: car, truck, bus
- 80k annotated frames from 100 video sequences
4.2. Implementation Details
- VGG-16, ResNet-101을 backbone으로 사용
- lr = 2e-3, 2e-4, 2e-5 epcohs(90, 120)
- weight decay = 0.0005
- momentum = 0.9
- batch-size = 32
- total epochs = 160
4.3. MS COCO Dataset
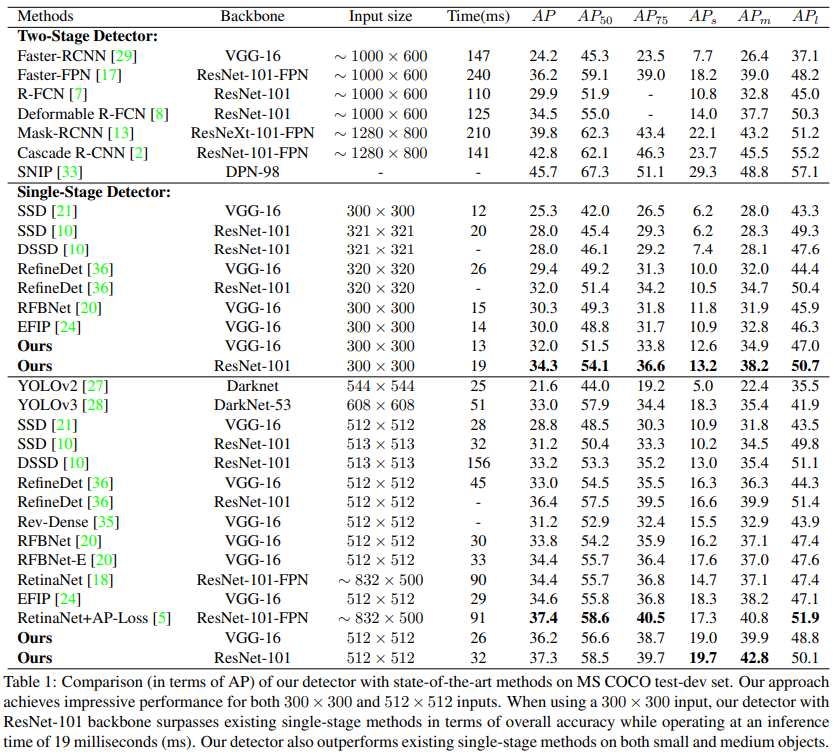
- Input size 300x300에서 baseline인 SSD보다 small, medium, large object를 잘 검출하며 RefineDet, RFBNet과 같은 기존 method보다 성능이 잘 나옴.
- Input size 512x512에서도 baseline SSD보다 높은 성능을 보여줌
- ResNet-101을 backbone으로 하는 RetinaNet, RetinaNet+AP-Loss보다는 성능이 조금은 떨어지기도 함, 그러나 inference speed 측면에서 더 빠름
- two-stage method들이 정확도는 더 높지만 input size가 크기 때문에 computation cost 또한 커지며 inference speed 역시 100 ms 이상 걸림, 그러나 우리가 제안하는 방법은 accuracy도 괜찮게 나오고 speed 측면에서 훨씬 효율적임
Qualitative Analysis
- MS COCO dataset에는 small size object가 41%를 차지하기 때문에 small object로 성능을 평가하는 것이 더 적합하다고도 볼 수 있음
- 여기서 small object의 기준은 object instance area < 32^2인 경우를 small object라고 함
VGG-16을 backbone으로 하는 baseline SSD(top row)와 our approach(bottom row)의 error를 분석
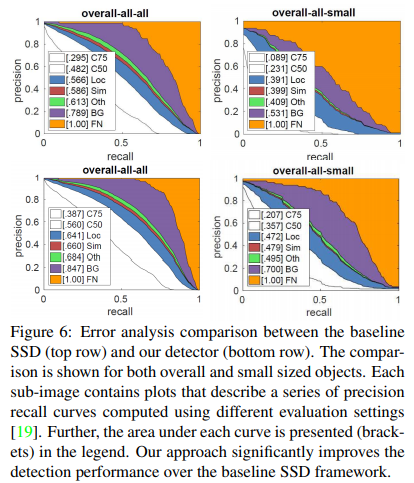
- C75 = IoU 0.75
- C50 = IoU 0.5
- Loc = poor localization
- Sim = similar category
- Oth = others
- BG = background
- e.g.) baseline SSD에서 IoU=0.5일 때, AP는 0.482가 나오지만 background false positive를 removing했을 때 0.789로 improve됨
- our approach를 사용하면 IoU=0.5일 때, AP=0.560이 나오고 마찬가지로 background false positive를 removing했을 때 0.847로 improve되어 baseline SSD보다 성능이 우수함
small object detection에서도 SSD보다 AP가 더 잘나옴
Ablation Study
논문에서 제안하는 LSN과 Bi-directional scheme를 썻을 때 모든 케이스에서 성능 향상이 이루어짐. 특히 small, medium object를 검출하는 것이 굉장히 어려운 문제였지만 LSN과 Bi-directional 구조를 통해 성능 향상을 이끌어냄
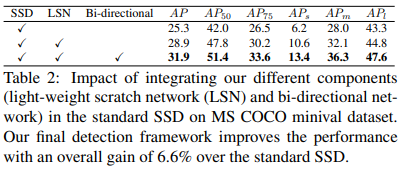
- LSN feature를 SSD의 different stage feature와 integrating하여 비교했을 때도 성능 향상이 있었지만 LSN feature를 higher layer와 integrating했을 때 성능 향상이 가장 크게 이루어짐
- LSN feature대신 SSD에서 shallow feature를 가져와서 integrating해봤는데 LSN feature를 사용하는 것보다 안 좋았음. 즉, pre-trained VGG에서 뽑아낸 feature가 아닌 training from scratch를 통해 feature를 뽑아서 integrating하는 것이 더 중요함
- 또한 제안하는 Bi-directional 구조를 SSD-FPN과 비교했을 때 더 높은 성능 향상이 이루어짐
LSN을 사용하지 않고 Bottom-up, Top-down scheme에서 connection구조를 다르게 적용했을 때 비교
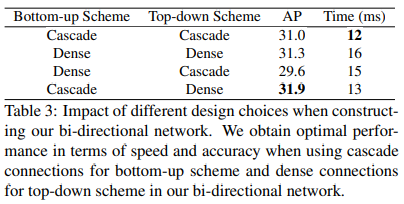
- Bottom-up, Top-down Scheme에서 Cascade 방식을 썼을 때 optimal speed가 나오지만 accuracy는 조금 떨어짐
- Bottom-up, Top-down Scheme에서 Dense 방식을 썼을 때 성능은 조금 올라가나 computational overhead가 발생함
- Bottom-up scheme에선 Cascade, Top-down scheme에선 Dense 방식을 썼을 때 optimal performance
- 따라서 accuracy, speed에 따라 top-down scheme의 design choice를 다르게 선택할 수 있음
4.4. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Dataset
UAVDT dataset에서 evaluation
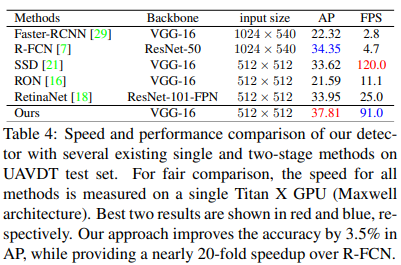
기존의 two-stage or single-stage method들보다 성능더 좋고 속도도 잘 나옴
5. Conclusion
- 새로운 single-stage object approach를 제안한다.
- standard SSD를 기반으로 light-weight scratch network(LSN)과 bi-directional network를 추가함
- LSN은 training from scratch 되므로 기존 standard SSD pre-trained backbone에서 만들어지는 feature에 대해 complementary feature를 추출할수 있음
- Bi-directional network는 low&mid level feature와 high-level semantic information이 detection network안에서 circulate될 수 있게 만들어줌
- MS COCO, UAVDT dataset에서 시간과 정확도를 고려했을 때에도 효율적이면서 superior result를 보여줌